09
08/2022
Agriculture, like the rest of economic activities, generates greenhouse gas emissions.In Catalonia, the volume of emissions in this sector is behind the energy, transport and industry.At the same time, he is a victim of climate change, because he suffers the consequences of meteorological phenomena such as droughts, floods or frosts, which will be increasingly extreme and frequent.Now, what is often not explained is that agriculture can play a crucial role to mitigate planetary warming thanks to the ability of the soil and the crops to fix and absorb carbon.
Plants continually absorb carbon dioxide generated by human activity through photosynthesis and, as a result, biomass occurs;When they die and break down, the living organisms of the soil such as bacteria, fungi or earthworms, among others, transform them into organic matter, a carbon rich material that retains water and nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen insoil.It is estimated that Catalan agricultural soils, which occupy 33% of the territory, contain both carbon and the one that Catalonia broadcasts in 4 years.It is a significant amount that could still be greater if carbon fixation and mitigation of greenhouse gases in agricultural practices in agricultural practices will be implemented.
As the initiative "4 per 1000" points out, launched by France in the COP15, if the organic carbon of agricultural and forest soils around the world increased by 0.4% per year (or, what is the same, in a 4 ‰), it would be more than the annual increase in CO2 emissions.Along these lines, the Yagroalimentarias Research Institute (IRTA), attached to the Department of Climate Action, Food and Rural Agenda (DACC) of the Generalitat de Catalunya, coordinates and leads several projects to determine what types of cultivation and what agricultural practices allow kidnappingMore carbon on the soil and in the woody structures of tree crops.
«All crops absorb carbon during the day through photosynthesis;At night, however, they release only one part, ”explains Robert Savé, emeritus researcher of the IRTA fruit growing program and one of the authors of the map of organic carbon reserves in the agricultural soils of Catalunya.«Woody crops, such as vineyard or olive.For example, it is estimated that the olive tree captures three times more carbon than a carrasco pine forest, ”says Savé.The IRTA expert points out that there are also differences according to the types of soils: the drySo much, the decomposition of organic matter, a part of which is transformed into carbon dioxide that is released to the atmosphere.
Or of Chicago Crit Care Nephrologist and BBQ Master @jaykoyner Tells Us How To Prevent Aki at The @asnkidney Board R ... https: // t.CO/PV66imjavo
— Roger Rodby Wed Jul 21 20:04:34 +0000 2021
Best practices, collected in a guide
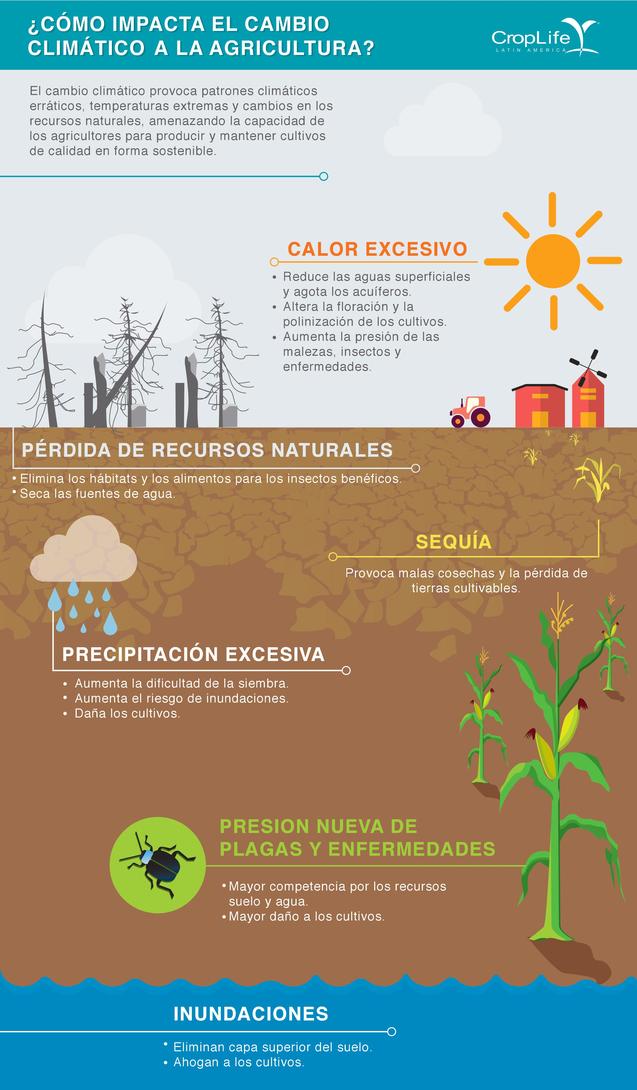
The power of absorption and carbon kidnapping of soils and crops is amplified according to the management and management of the same.The Guide to Good Agricultural Practices, in whose writing the IRTcitrus, vine and rice.Among the practices that are collected and that favor the kidnapping of carbon are, for example, incorporate the remains of pruning or crop in the soil, or label the minimum or even not work.Thus, as the guide collects, it is estimated that incorporating pruning remains can increase organic carbon content by 60% in the surface layers of the soil.
"These practices, on the one hand, that part of the carbon synthesized during crop is reincorporated to the agrosystem and, on the other, slow down the decomposition of organic matter, which prevents the return of carbon to the atmosphere," explains the researcher of theMarinas and Continental Program of Irta Maite Martínez-Eixarch, one of the guide authors.
In the fight against climate change, the involvement of the sector is indispensable and, in this sense, one of the leaders is the winemakers.The Institute has various initiatives with wine companies, to which it provides advice when making decisions so that they can make the maximum performance of soil moisture.It also has years of experience in projects about vineyard and climate change.A good sample of this is the Vitimpact Project: Contribution to the Environmental Evaluation of Viticulture, developed with the University of Lleida (UDL), which “has provided utility information in the progress of knowledge regarding the influence of the soil, availability Water, the fertilization and biodiversity of the microbiota of the soil in the direct emissions of greenhouse gas in the cultivation of the vineyard in conditions of Mediterranean dry land, ”explains happiness in Herralde, researcher of the IRTA fruiting program and one of the authors of the project.
More carbon, more fertility
The increase in carbon fixation capacity by soils makes them more fertile and resilient and, therefore, more productive, something that helps supply food in an exponential growing world: it is expected that by 2050 there are inThe planet 10.000 million people and that food demand increases up to 60%.This, in environmental conditions that, according to the first report of climate change in the Mediterranean (Mar1) of the Mediterranean Experts NetMediterranean zone.The supply of quality food, insurance and affordable is, together with the mitigation of global warming, the other great challenge of agriculture.The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals include these challenges in SDGs 2 (zero hunger) and 13 (climate action), which note that agricultural soils are allies for food security and to deal with climate change.

- 763
- How to get rid of a phosphorus brand in clothes
Related Articles
The scanner of... Pilar Rubio: we get the truth (and what they don't want to be known) from celebrities
02/02/2022The halo of mystery that surrounds celebrities is always part of their charm, and it is that we never know where they are going to turn out, if they really tell us the truth or if they are people like us when...
30 Best Men's High Neck Sweater for you
24/02/2022Home » Clothing » 30 Best Men's Turtleneck Sweater for youClothesJenaro CardoApril 25, 2021 178 Views0SaveSavedRemoved 0 Improving technology only needs to increase the level of competition in ca...
50 Best Bedspreads 135 in 2021 - Based on 996 Customer Reviews and 66 Hours of Testing
18/04/2022Yes, Reig Martí Blue QUILT Bedspread for Bed 135 cm VASSILE is one of the most sought-after bedspreads for beds 135, it does not satisfy everyone's needs and it can be a bit expensive. That's why, after passing 66...
30 Top Rated 18th Birthday Balloons
11/05/2022Home » Office Products » 30 Top Rated 18th Birthday Balloons Office Products Gervasio Teodoro January 25, 2022 36 Views0 SaveSavedRemoved 0 Are you wandering around the market to...